c
DAW Explained: What Is It + 5 Things You Can Make With It
“DAW” is one of the most renowned terms in the production field.
There is a good reason for its fame.. it is the center of music production.
In this article called “DAW Explained” we will see everything you need to know about DAWs.
DAW Explained: What is it?

A DAW (Digital Audio Workstation) is the central workplace of every music producer.
It is a single software that allows us to do absolutely everything to produce our songs. Record, edit, mix, automate, looping, master, sample, etc.
It’s often confused with “recording software”, but in reality, an audio recording software does just that.. records audio. Instead, the possibilities of things you can do in a DAW are almost limitless.
5 Things You Can Do With a DAW
A DAW allows us to do a lot of audio-related tasks.
5 of those production things that a DAW can do are:
- Record audio tracks
- Use VST plugins
- Connect your MIDI controllers
- Using loops and samples
- Mix and master
PS: You can do many more things with a DAW, but these are the essentials to understand how it works.
1. Record audio tracks
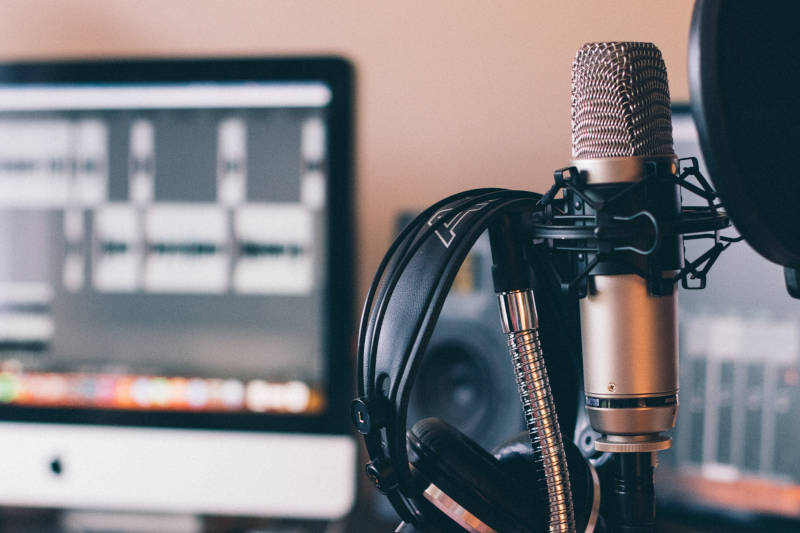

You can make multitrack recordings and handle it all from a single panel with a DAW.
The proper way to make recordings in a DAW is through an audio interface. It’s our intermediary with the microphones and instruments.
From the DAW, you can control the audio interface via the USB connection and make recordings of instruments and voices.
2. Use VST plugins
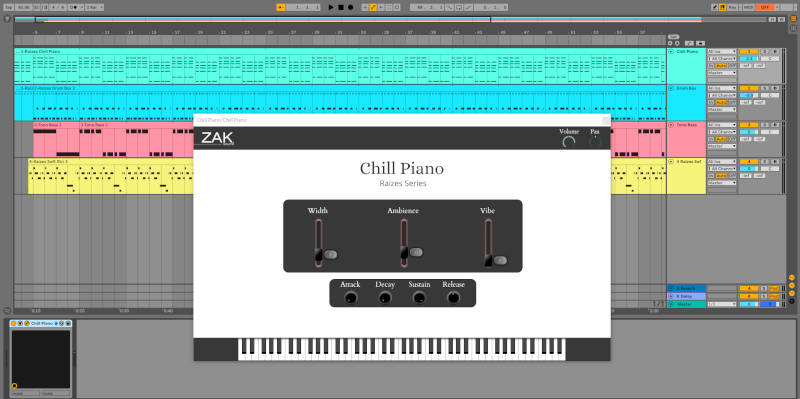
One of the coolest things to do in a DAW is using VST plugins.
VST plugins are divided into two categories:
- Instrument plugins: They are the virtual version of the instruments. You can play and record any instrument using a VST plugin in a DAW. Pianos, basses, drums, saxophones, synthesizers, and whatever else you can imagine.
- Effects plugins: These are emulations of effects such as reverb, delay, chorus, distortion, filters, etc. Plus, there are effects plugins for mixing, mastering, and doing a lot more.
All DAWs come with a stock of plugins out of the box. Some more and some less. But that’s not that important since you can install plugins from third-party providers. Here at ZAK Sound, we build instrument plugins (and many free).
You can write the note patterns of the instrument plugins with the mouse, but it’s better to record it with a MIDI keyboard to get a human feel (explained in the next title).
3. Connect your MIDI controllers
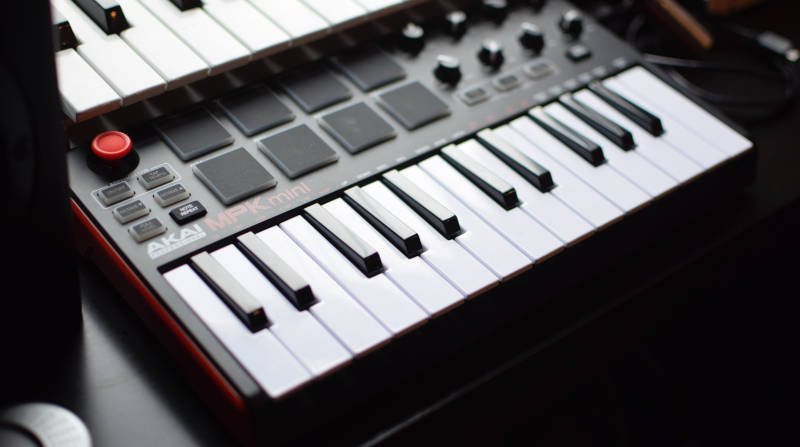

You can connect all your MIDI gear to the computer (directly via USB or the audio interface) and control it from the DAW.
There are several types of MIDI controllers:
- MIDI keyboards: They are the most popular type of controller; you can play and record note patterns with them. You can play or record any instrument plugin with the MIDI keyboard, like an acoustic piano or an orchestral violin plugin.
- Drum Pad Controllers: Perfect for playing and recording drum patterns. Many MIDI keyboards come with drum pads, but you can also get a separate controller.
- Specific controllers for each DAW: There are controllers designed to work specifically with a particular DAW. For example, the Launchpad for Ableton or the Akai Fire for FL Studio. These are good to use many DAW functions on a physical gear and to work more efficiently.
4. Using loops and samples
Another great thing you can do with a DAW is use loops and samples.
For example, if you don’t know how to make drum patterns manually, you can look for ready-made drum loops. Drag it into the DAW, set the tempo (BPM), and the audio will adapt to your project (in each DAW, it’s set up differently).
Another very popular thing in some styles is sampling. For example, if you like how the voice of a singing parrot sounds, you can record it and sample it to make a melody with its voice.
Some DAWs like FL Studio have helpful functions to sample anything very simply.
5. Mix and master
Finally, we have the most essential thing to make our production sound professional: mixing and mastering.
The mixing process refers to the making of everything necessary for our song to sound balanced. This involves optimizing each track to be consistent with the rest of the mix. It is achieved through volume adjustments, equalization, filters, compression, etc.
The final process is mastering. Refers to making slight changes to the final stereo audio to make it ready for distribution.
All of this can be done in the DAW.
Most used DAWs by producers
There are hundreds of DAWs on the market.
They are all excellent and offer a unique solution for each type of use.
- Ableton Live: One of the most popular DAWs today. Powerful production tools and unique functions like “Live Looping“.
- FL Studio: Initially famous for EDM producers, it is a great DAW with a beautiful view for handling loops, sampling, and many powerful audio editing functions.
- Reaper: Loved by many alternative artists, this is a DAW that offers us a lot at a low price.
- Cubase: One of the most classic DAWs when it comes to production.
- Logic Pro: Popular among macOS users, it ranks as one of the most versatile options for Apple.
- Studio One: Relatively new DAW with a visual interface and a good workflow.
- Bitwig: It has a design and functionality similar to Ableton Live; it’s an alternative.
- Pro Tools: Prestigious in professional studios, Pro Tools offers unique production and post-production tools.
DAW Explained, Summary: The Center of Production
So.. yes, the DAW is one of the most important pieces for producers. It’s a robust software for both professional studios and home studios.
You can say that it’s the center of music production.
It makes our productions possible to achieve and helps us get the final result we want.
But of course, it takes time to learn. It is not overnight. Therefore, you need to choose a DAW and learn as much as possible from it.




 We use cookies to enhance your experience, analyze site traffic, and personalize content. By accepting, you help us show you more relevant offers and improve your overall experience.
We use cookies to enhance your experience, analyze site traffic, and personalize content. By accepting, you help us show you more relevant offers and improve your overall experience.